-
静态链表的意义不是很大,主要原因,数据存储在栈上,栈的存储空间有限,不能动态分配。所以链表要实现存储的自由,要动态的申请堆里的空间。
-
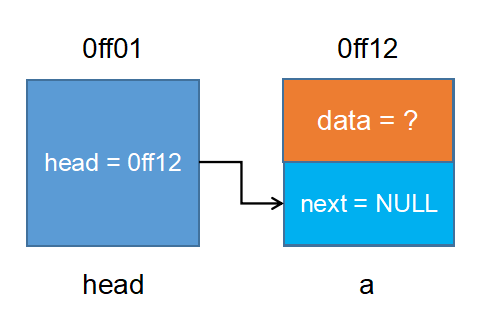
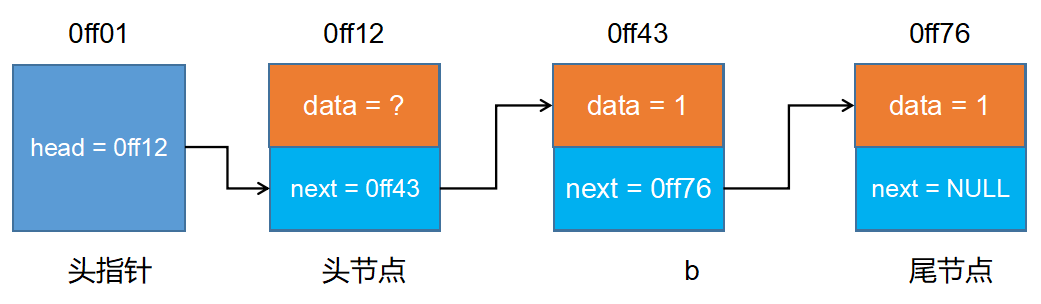
有一个点要说清楚,我们的实现的链表是带头节点。至于,为什么带头节点,需等大家对链表有个整体的的认知以后,再来体会,会更有意义。
-
空链表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 1.定义链表节点
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Node;
int main()
{
Node *head = createList();
return 0;
}
// 创建空链表
Node *createList(){
// 1.创建一个节点
Node *node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(node == NULL){
exit(-1);
}
// 2.设置下一个节点为NULL
node->next = NULL;
// 3.返回创建好的节点
return node;
}- 非空链表
- 1.让新节点的下一个节点等于头结点的下一个节点
- 2.让头节点的下一个节点等于新节点
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 1.定义链表节点
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Node;
Node *createList();
void printNodeList(Node *node);
int main()
{
Node *head = createList();
printNodeList(head);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief createList 创建链表
* @return 创建好的链表
*/
Node *createList(){
// 1.创建头节点
Node *head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
head->next = NULL;
// 2.接收用户输入数据
int num = -1;
printf("请输入节点数据\n");
scanf("%i", &num);
// 3.通过循环创建其它节点
while(num != -1){
// 3.1创建一个新的节点
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cur->data = num;
// 3.2让新节点的下一个节点指向头节点的下一个节点
cur->next = head->next;
// 3.3让头节点的下一个节点指向新节点
head->next = cur;
// 3.4再次接收用户输入数据
scanf("%i", &num);
}
// 3.返回创建好的节点
return head;
}
/**
* @brief printNodeList 遍历链表
* @param node 链表指针头
*/
void printNodeList(Node *node){
Node *head = node->next;
while(head != NULL){
int currentData = head->data;
printf("currentData = %i\n", currentData);
head = head->next;
}
}- 1.定义变量记录新节点的上一个节点
- 2.将新节点添加到上一个节点后面
- 3.让新节点成为下一个节点的上一个节点
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 1.定义链表节点
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Node;
Node *createList();
void printNodeList(Node *node);
int main()
{
Node *head = createList();
printNodeList(head);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief createList 创建链表
* @return 创建好的链表
*/
Node *createList(){
// 1.创建头节点
Node *head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
head->next = NULL;
// 2.接收用户输入数据
int num = -1;
printf("请输入节点数据\n");
scanf("%i", &num);
// 3.通过循环创建其它节点
// 定义变量记录上一个节点
Node *pre = head;
while(num != -1){
// 3.1创建一个新的节点
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cur->data = num;
// 3.2让新节点链接到上一个节点后面
pre->next = cur;
// 3.3当前节点下一个节点等于NULL
cur->next = NULL;
// 3.4让当前节点编程下一个节点的上一个节点
pre = cur;
// 3.5再次接收用户输入数据
scanf("%i", &num);
}
// 3.返回创建好的节点
return head;
}
/**
* @brief printNodeList 遍历链表
* @param node 链表指针头
*/
void printNodeList(Node *node){
Node *head = node->next;
while(head != NULL){
int currentData = head->data;
printf("currentData = %i\n", currentData);
head = head->next;
}
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 1.定义链表节点
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Node;
Node *createList();
void printNodeList(Node *node);
void insertNode1(Node *head, int data);
void insertNode2(Node *head, int data);
int main()
{
// 1.创建一个空链表
Node *head = createList();
// 2.往空链表中插入数据
insertNode1(head, 1);
insertNode1(head, 3);
insertNode1(head, 5);
printNodeList(head);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief createList 创建空链表
* @return 创建好的空链表
*/
Node *createList(){
// 1.创建头节点
Node *head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
head->next = NULL;
// 3.返回创建好的节点
return head;
}
/**
* @brief insertNode1 尾插法插入节点
* @param head 需要插入的头指针
* @param data 需要插入的数据
* @return 插入之后的链表
*/
void insertNode1(Node *head, int data){
// 1.定义变量记录最后一个节点
Node *pre = head;
while(pre != NULL && pre->next != NULL){
pre = pre->next;
}
// 2.创建一个新的节点
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cur->data = data;
// 3.让新节点链接到上一个节点后面
pre->next = cur;
// 4.当前节点下一个节点等于NULL
cur->next = NULL;
// 5.让当前节点编程下一个节点的上一个节点
pre = cur;
}
/**
* @brief insertNode1 头插法插入节点
* @param head 需要插入的头指针
* @param data 需要插入的数据
* @return 插入之后的链表
*/
void insertNode2(Node *head, int data){
// 1.创建一个新的节点
Node *cur = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cur->data = data;
// 2.让新节点的下一个节点指向头节点的下一个节点
cur->next = head->next;
// 3.让头节点的下一个节点指向新节点
head->next = cur;
}
/**
* @brief printNodeList 遍历链表
* @param node 链表指针头
*/
void printNodeList(Node *node){
Node *head = node->next;
while(head != NULL){
int currentData = head->data;
printf("currentData = %i\n", currentData);
head = head->next;
}
}最后,如果有任何疑问,请加微信 leader_fengy 拉你进学习交流群。
开源不易,码字不易,如果觉得有价值,欢迎分享支持。